Where is medical marijuana legal? This question sparks a journey across the globe, revealing a tapestry of regulations as diverse as the plant itself. From countries embracing its potential to those still hesitant, the legal landscape shifts constantly. Imagine navigating this complex terrain, understanding not just where it’s permitted, but also the intricacies of cultivation, distribution, and consumption.
We’ll delve into the international stage, charting the course of legalization worldwide. Then, we’ll turn our attention to the United States, examining the patchwork of state laws and the federal government’s perspective. Canada offers a fascinating case study, with its established system providing valuable insights. Furthermore, we will explore the medical conditions that often find relief through cannabis, the role of healthcare professionals, and the implications for public health.
Finally, we’ll gaze into the future, anticipating the evolving trends and innovations that will shape the medical marijuana industry.
Discovering the Current Status of Medical Marijuana Legalization Worldwide is Important

Understanding the global landscape of medical marijuana legalization is crucial. It provides insight into the evolving attitudes towards cannabis, its therapeutic potential, and the complex interplay of societal, political, and economic factors shaping its acceptance. This knowledge is essential for patients, healthcare professionals, policymakers, and anyone interested in the future of medicine and drug policy.
Detailing the Global Landscape of Medical Marijuana Legality
The legality of medical marijuana varies significantly across the globe, reflecting diverse cultural perspectives, regulatory approaches, and levels of scientific understanding. The following overview presents a snapshot of the current situation.Countries where medical marijuana is fully legal include:
Canada
Legalized medical cannabis in 2001, with a robust regulatory framework.
Uruguay
Legalized medical cannabis in 2013, with a focus on regulating the entire supply chain.
Thailand
Legalized medical cannabis in 2018, expanding access through traditional medicine practices.Countries where medical marijuana is partially legal include:
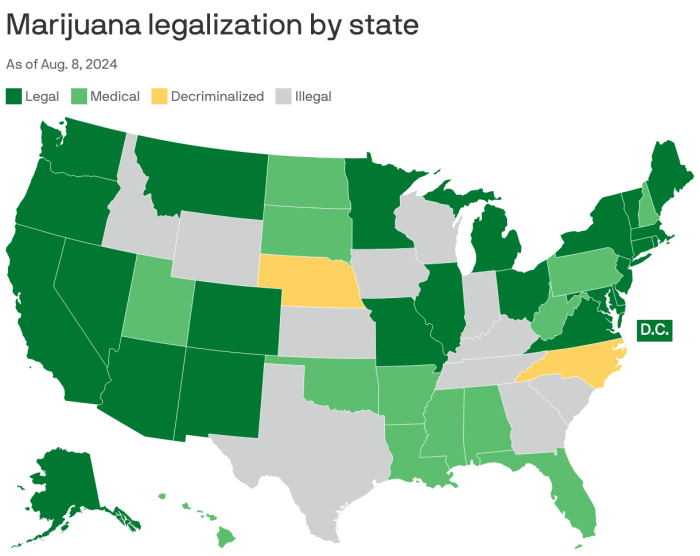
United States
Medical cannabis is legal in many states, but not at the federal level, creating a complex patchwork of regulations.
Australia
Medical cannabis is legal nationwide, but access and regulations vary by state and territory.
Germany
Medical cannabis is legal with a prescription, with cultivation and distribution heavily regulated.
Italy
Medical cannabis is legal, but cultivation and production are limited.
United Kingdom
Medical cannabis is legal with a prescription from a specialist doctor.
Israel
Medical cannabis is legal, with a well-established medical cannabis industry.Countries where medical marijuana is illegal include:
China
Cannabis is illegal for all uses.
Japan
Cannabis is illegal for all uses.
Russia
Cannabis is illegal for all uses.
Indonesia
Cannabis is illegal for all uses.
Saudi Arabia
Cannabis is illegal for all uses.
Comparing Legal Frameworks and Regulations
Different legal frameworks dictate the cultivation, distribution, and consumption of medical marijuana. These frameworks are often influenced by cultural norms, public health concerns, and economic considerations. Here’s a comparative look at some key regulatory aspects:
| Legal Framework Aspect | Fully Legal Countries (Example: Canada) | Partially Legal Countries (Example: United States – State Level) | Illegal Countries (Example: China) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivation | Licensed producers cultivate cannabis under strict regulations. Home cultivation may be permitted, with limits. | Cultivation is often regulated by state-level licenses, with varying restrictions on the number of plants, location, and security. | Cultivation is illegal, with severe penalties. |
| Distribution | Distribution is typically handled by licensed retailers, often with online ordering and delivery options. | Distribution systems vary by state, including licensed dispensaries, delivery services, and sometimes pharmacies. | Distribution is illegal, with severe penalties. |
| Consumption | Consumption is allowed in designated areas, often with restrictions on public use. Edibles, extracts, and topicals are available. | Consumption rules vary by state, often restricting public use. Edibles, extracts, and topicals are available, with some states imposing potency limits. | Consumption is illegal, with severe penalties. |
| Patient Access | Patients need a medical document from a healthcare practitioner. Products are widely available. | Patients need a recommendation or certification from a healthcare provider, and access varies based on state regulations. | Access is nonexistent. |
Elaborating on Common Challenges and Obstacles
The implementation and enforcement of medical marijuana laws face numerous challenges. These hurdles can hinder patient access, undermine public safety, and create legal and economic complexities.Some common obstacles include:
- Regulatory Complexity: Establishing clear and effective regulations that balance patient access with public safety is a constant challenge. This includes setting standards for product testing, labeling, and packaging.
- Banking and Financial Restrictions: Federal laws in some countries make it difficult for cannabis businesses to access banking services, hindering their ability to operate legally and pay taxes. This forces many businesses to deal in cash, creating security risks.
- Lack of Research and Data: Insufficient research on the long-term effects of medical marijuana and the efficacy of different strains and dosages creates uncertainty among healthcare professionals and patients. More scientific data is needed.
- Stigma and Social Acceptance: Despite growing acceptance, stigma surrounding cannabis use persists, making it difficult for some patients to seek treatment and for policymakers to enact progressive laws. Addressing misinformation and promoting education are essential.
- Enforcement Challenges: Law enforcement agencies face challenges in enforcing medical marijuana laws, particularly in areas where recreational use is also legal. Distinguishing between legal and illegal activities can be difficult.
- International Conflicts: The lack of harmonization in international drug policies can create challenges for cross-border trade and research.
Understanding the Legal Frameworks Governing Medical Marijuana in the United States is Critical: Where Is Medical Marijuana Legal
Navigating the world of medical marijuana in the US can feel like traversing a complex maze. The legal landscape is a patchwork quilt, with each state crafting its own rules and regulations. This creates a fascinating, yet often confusing, situation for patients, providers, and businesses alike. Understanding these nuances is not just helpful; it’s essential for anyone seeking to utilize medical marijuana legally and responsibly.
Variations in Medical Marijuana Laws Across US States
The United States operates under a system where individual states have the power to legislate on matters not explicitly reserved for the federal government. This has led to a wide variety of approaches to medical marijuana. The variations extend to qualifying conditions, permissible forms of cannabis, and the operational structure of the industry.
- Qualifying Medical Conditions: The list of conditions that qualify for medical marijuana varies significantly. Some states have expansive lists, including conditions like chronic pain, anxiety, and PTSD. Other states have more restrictive lists, focusing on conditions like cancer, HIV/AIDS, and epilepsy. For instance, California, a pioneer in medical marijuana, has a relatively broad list, while states like Texas have a more limited program, focusing on specific conditions like intractable epilepsy.
- Permitted Forms of Cannabis: The forms of cannabis allowed also differ. Some states permit only low-THC, high-CBD products, while others allow for a full range of products, including flower, edibles, concentrates, and topicals. The permitted forms also affect the potency and dosage of the products available to patients.
- Regulations on Dispensaries and Cultivation: States regulate the cultivation, processing, and sale of medical marijuana. Some states have a highly regulated system with strict licensing requirements, while others have a more open market. These regulations impact the accessibility and cost of medical marijuana for patients.
The Federal Government’s Stance on Medical Marijuana
The federal government’s position on medical marijuana creates a layer of complexity. While many states have legalized medical marijuana, it remains illegal under federal law. This discrepancy has significant implications for state-level legalization efforts.
The primary federal law regarding cannabis is the Controlled Substances Act (CSA), which classifies marijuana as a Schedule I drug, alongside substances like heroin. This means the federal government views marijuana as having a high potential for abuse and no currently accepted medical use.
This federal stance creates several challenges:
- Banking Restrictions: Federal laws make it difficult for cannabis businesses to access traditional banking services. Banks are hesitant to work with businesses that handle a substance that is illegal at the federal level, leading to cash-only businesses and security concerns.
- Interstate Commerce: The federal prohibition also restricts the interstate commerce of marijuana. Cannabis products grown and sold legally in one state cannot be transported across state lines, even to another state where medical marijuana is legal.
- Federal Enforcement: While the federal government has generally taken a hands-off approach to enforcing marijuana laws in states where it is legal, it retains the power to intervene. This uncertainty can create anxiety for both patients and businesses.
Despite these challenges, the federal government’s stance has been evolving. The Department of Justice (DOJ) under various administrations has issued guidance, such as the Cole Memorandum, which Artikeld a policy of non-interference with state-legalized marijuana programs. However, this guidance can be rescinded or altered, creating a fluctuating legal environment.
The evolving nature of federal policy underscores the importance of staying informed about legal developments.
Process for Obtaining a Medical Marijuana Card
Obtaining a medical marijuana card typically involves a multi-step process. While the specifics vary by state, the general steps remain consistent. Understanding this process is critical for anyone considering using medical marijuana for therapeutic purposes.
Here’s a breakdown of the typical process:
- Determine Eligibility: The first step is to determine if you meet the state’s qualifying conditions. This information is usually available on the state’s health department website or a dedicated medical marijuana program website.
- Obtain a Recommendation: You will need a recommendation from a licensed physician. The physician must be registered with the state’s medical marijuana program and be able to diagnose your qualifying condition. The physician will assess your medical history and determine if medical marijuana is an appropriate treatment option.
- Complete an Application: Once you have a recommendation, you will need to complete an application for a medical marijuana card. The application process typically involves submitting personal information, the physician’s recommendation, and any required fees.
- Submit Documentation: You will need to provide documentation to verify your identity and residency. Acceptable forms of documentation may include a driver’s license, state-issued ID, and proof of address.
- Receive Your Card: If your application is approved, you will receive a medical marijuana card. The card will allow you to purchase medical marijuana from licensed dispensaries. The time it takes to receive your card varies by state.
It’s important to remember that the rules and regulations are subject to change. Always consult the official state government websites for the most up-to-date information. For example, in New York, the application process is now streamlined, with online portals making it easier to apply. However, in states like Florida, the process may require visiting a physician in person, and the approval times can vary significantly.
These differences highlight the importance of understanding the specific regulations in your state.
Examining the Canadian Medical Marijuana System Offers Insights
Canada’s approach to medical marijuana provides a fascinating case study in how a nation can navigate the complexities of cannabis legalization. It offers a unique perspective on patient access, regulatory frameworks, and the evolution of the medical cannabis industry. Understanding the Canadian system allows for a deeper appreciation of the various models implemented worldwide and their impact on both patients and the broader market.
Specific Regulations Surrounding Medical Marijuana in Canada
Canada’s medical marijuana program is built upon a foundation of federal regulations, with oversight from Health Canada. The system prioritizes patient access through licensed producers.The key aspects of the regulations are:
- Licensed Producers: These are entities authorized by Health Canada to cultivate, process, and sell cannabis products. They operate under strict guidelines to ensure quality control and product safety. The licensing process involves rigorous inspections and adherence to Good Production Practices (GPP).
- Patient Access: Patients with a medical document (similar to a prescription) from a healthcare practitioner can access medical cannabis. They can either purchase products directly from licensed producers or register to grow a limited number of plants themselves.
- Product Variety: Licensed producers offer a wide range of cannabis products, including dried flower, oils, capsules, and edibles. This diversity caters to different patient needs and preferences.
- Quality Control: Health Canada mandates rigorous testing of cannabis products for cannabinoid content, contaminants, and pesticides. This ensures product consistency and patient safety.
- Record Keeping and Reporting: Licensed producers are required to maintain detailed records of their operations, including cultivation, processing, and sales. They also must report to Health Canada on a regular basis.
Comparing the Canadian System with the US System
Comparing the Canadian and US systems reveals significant differences in access, quality control, and pricing. The US system is a patchwork of state-level regulations, while Canada operates under a unified federal framework.Here’s a comparison:
- Access: In Canada, access is primarily through licensed producers and, in some cases, personal cultivation. In the US, access varies widely by state, with some states allowing medical use and others not. Access often involves state-licensed dispensaries.
- Quality Control: Canada’s system has a more centralized quality control framework, with federal oversight and mandatory testing. The US system varies significantly by state, with some states having robust testing programs and others lacking them.
- Pricing: Pricing in Canada is influenced by market competition among licensed producers and government taxation. In the US, pricing varies widely based on state regulations, taxes, and the competitive landscape of the local market.
- Federal vs. State Legalization: The US system operates under a legal gray area at the federal level, even in states where cannabis is legal. This can create challenges for businesses and patients. Canada’s federal legalization has streamlined operations.
Impact of Federal Legalization on the Medical Marijuana Industry in Canada
Federal legalization in Canada had a transformative effect on the medical marijuana industry. It fueled market growth and spurred innovation.Here are some key impacts:
- Market Growth: Legalization expanded the market significantly, attracting both medical and recreational users. This led to increased sales and revenue for licensed producers. The initial years saw rapid expansion, followed by market consolidation.
- Innovation: The legal framework encouraged innovation in product development, cultivation techniques, and delivery methods. Companies invested in research and development to create new cannabis strains, extracts, and consumption devices.
- Investment and Funding: Legalization attracted substantial investment from both domestic and international sources. This funding supported the growth of licensed producers, research initiatives, and infrastructure development.
- Employment Opportunities: The industry created numerous employment opportunities in cultivation, processing, distribution, and retail. This contributed to economic growth and job creation across Canada.
- Regulatory Refinement: The government continues to refine the regulations based on experience and feedback from stakeholders. This includes addressing issues such as product labeling, packaging, and the promotion of responsible use.
The Canadian experience offers valuable lessons for other countries considering medical marijuana legalization. The emphasis on patient access, quality control, and a robust regulatory framework has helped to establish a safe and accessible medical cannabis market.
Exploring the Medical Conditions that Typically Qualify for Medical Marijuana is Beneficial
Medical marijuana, a topic of significant interest and evolving legal landscapes, presents a complex intersection of scientific inquiry, patient needs, and regulatory frameworks. Understanding the conditions for which medical marijuana is often considered and the potential benefits, risks, and side effects associated with its use is crucial for informed decision-making. This exploration delves into some of the most common medical conditions where medical marijuana is employed, offering a balanced perspective on its therapeutic potential.
Chronic Pain Management
Chronic pain, a persistent and often debilitating condition, affects millions globally. It can stem from various sources, including arthritis, fibromyalgia, neuropathy, and cancer. Medical marijuana has emerged as a potential therapeutic option for managing chronic pain, offering an alternative or adjunct to traditional pain medications.The potential benefits of medical marijuana for chronic pain include:
- Pain Relief: Cannabinoids, the active compounds in marijuana, interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in pain regulation. This interaction can reduce pain signals and provide relief.
- Reduced Reliance on Opioids: Some patients have reported reducing or eliminating their opioid use after incorporating medical marijuana into their treatment plan. This is significant because it can help reduce the risks associated with opioid use, such as addiction and overdose.
- Improved Sleep: Chronic pain often interferes with sleep. Medical marijuana can promote relaxation and improve sleep quality, which can further alleviate pain and improve overall well-being.
- Enhanced Mood: Chronic pain can lead to depression and anxiety. Medical marijuana may improve mood and reduce anxiety, improving the patient’s quality of life.
Neurological Disorders
Certain neurological disorders, characterized by dysfunction of the nervous system, may benefit from medical marijuana. These conditions include multiple sclerosis (MS), epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease. The potential of medical marijuana lies in its ability to interact with the endocannabinoid system, potentially mitigating some symptoms.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS):
- Symptom Management: Medical marijuana can help reduce muscle spasticity, a common symptom of MS, improving mobility and reducing pain.
- Pain Relief: Cannabinoids can alleviate neuropathic pain associated with MS.
- Improved Bladder Control: Some patients experience improvements in bladder control.
- Epilepsy:
- Seizure Reduction: Certain strains of medical marijuana, particularly those high in cannabidiol (CBD), have been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures in some individuals, especially those with treatment-resistant epilepsy.
- Parkinson’s Disease:
- Symptom Relief: Medical marijuana may help reduce tremors, improve motor control, and alleviate muscle stiffness.
- Pain Management: It can help manage pain associated with Parkinson’s.
Cancer-Related Symptoms
Medical marijuana has shown promise in managing various symptoms associated with cancer and its treatments. These symptoms include nausea, vomiting, pain, and loss of appetite. The use of medical marijuana can significantly improve the quality of life for cancer patients.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Medical marijuana, particularly through the use of cannabinoids like THC, has been shown to be effective in reducing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
- Pain Management: Medical marijuana can help manage cancer-related pain, including pain from the disease itself and pain caused by treatments.
- Appetite Stimulation: Cancer treatments often lead to loss of appetite. Medical marijuana can stimulate appetite, helping patients maintain their weight and nutritional status.
- Improved Sleep: Medical marijuana can help cancer patients with sleep disturbances, which can be caused by the disease or its treatments.
Mental Health Conditions
Medical marijuana is sometimes used to manage symptoms of certain mental health conditions, although its use in this area remains controversial and requires careful consideration. These conditions include anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and depression.
- Anxiety: Some studies suggest that low doses of certain cannabinoids, such as CBD, may help reduce anxiety.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Medical marijuana may help alleviate symptoms of PTSD, such as nightmares, flashbacks, and anxiety.
- Depression: While more research is needed, some individuals with depression have reported improvements in mood and a reduction in depressive symptoms with the use of medical marijuana.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Medical Marijuana
While medical marijuana may offer therapeutic benefits for various medical conditions, it is important to acknowledge the potential risks and side effects associated with its use. A balanced perspective is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Cognitive Impairment: Medical marijuana can impair cognitive function, including memory, attention, and coordination, particularly with high-THC strains.
- Psychiatric Effects: In some individuals, particularly those with a predisposition to mental illness, medical marijuana use may worsen anxiety, depression, or psychosis.
- Respiratory Issues: Smoking marijuana can irritate the lungs and lead to respiratory problems, such as bronchitis and chronic cough. The method of consumption affects the risk of respiratory problems.
- Addiction: Regular use of marijuana, especially high-THC strains, can lead to dependence and addiction.
- Drug Interactions: Medical marijuana can interact with other medications, potentially affecting their efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Medical marijuana can increase heart rate and blood pressure, which may pose a risk to individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
Analyzing the Role of Doctors and Healthcare Professionals in the Medical Marijuana Process is Crucial
The journey of a patient seeking medical marijuana is a collaborative effort, a dance between the patient and their healthcare provider. It’s not just about getting a prescription; it’s about a careful assessment, ongoing support, and a commitment to patient well-being. Understanding the roles, responsibilities, and limitations of these medical professionals is paramount for anyone considering this treatment option.
The Role of Doctors in Recommending and Prescribing Medical Marijuana
Doctors act as gatekeepers, guides, and guardians in the medical marijuana process. Their involvement is multifaceted, ensuring patient safety and adherence to legal regulations.
- Assessment of Medical History and Current Condition: Before any recommendation, a thorough review of the patient’s medical history, current symptoms, and any existing treatments is essential. This includes a physical examination and, potentially, the ordering of diagnostic tests to establish a clear diagnosis.
- Determining Suitability: Doctors evaluate whether medical marijuana is a potentially beneficial treatment option for the patient’s specific condition. This involves considering the potential benefits against the risks, including any potential drug interactions or contraindications.
- Providing Recommendations and Certifications: In jurisdictions where medical marijuana is legal, doctors provide written recommendations or certifications, which are required for patients to obtain medical marijuana. The specifics of these documents vary by location, but they typically include the patient’s diagnosis, the recommended dosage, and the form of marijuana (e.g., oil, edibles, or flower).
- Patient Education: Educating patients about the potential benefits, risks, side effects, and legal aspects of medical marijuana is a crucial responsibility. This includes discussing different consumption methods, the importance of starting with a low dose, and the potential for interactions with other medications.
- Staying Informed: Healthcare professionals must remain updated on the latest research and guidelines regarding medical marijuana. This involves continuous professional development and a commitment to evidence-based practice. The evolving nature of the research means that staying current is a continuous process.
- Adhering to Legal and Ethical Standards: Doctors are bound by legal and ethical guidelines that govern the prescribing of medical marijuana. This includes ensuring that recommendations are based on a legitimate medical need and that they comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
“The doctor’s role isn’t just about writing a prescription; it’s about being a partner in the patient’s care, guiding them through a complex landscape and ensuring their safety and well-being.”
Consulting with a Healthcare Professional to Determine if Medical Marijuana is a Suitable Treatment Option
The initial consultation is a pivotal step. It’s where the patient and the doctor begin to explore the potential of medical marijuana as a treatment option.
- Preparing for the Consultation: Patients should gather all relevant medical records, including previous diagnoses, treatments, and current medications. They should also be prepared to discuss their symptoms, their experiences with other treatments, and their expectations regarding medical marijuana.
- The Consultation Process: The doctor will conduct a comprehensive evaluation, including a review of the patient’s medical history, a physical examination, and a discussion of the patient’s symptoms and goals. The doctor will then assess whether medical marijuana is a suitable option, considering the patient’s specific condition, potential benefits, and risks.
- Discussing Alternatives: The doctor should discuss other treatment options, including both conventional and alternative therapies, and compare their potential benefits and risks with those of medical marijuana. This helps the patient make an informed decision.
- Informed Consent: Patients should receive a thorough explanation of the potential benefits, risks, and side effects of medical marijuana. They should also be informed about the legal aspects of medical marijuana in their jurisdiction. Informed consent is a critical aspect of ethical medical practice.
- Making an Informed Decision: Based on the information provided by the doctor, the patient will decide whether to pursue medical marijuana treatment. The doctor’s role is to provide guidance and support, but the ultimate decision rests with the patient.
Importance of Ongoing Monitoring and Follow-Up Care for Patients Using Medical Marijuana
Medical marijuana treatment is not a one-time event; it requires ongoing monitoring and follow-up care to ensure its effectiveness and safety.
- Regular Check-ups: Patients should attend regular check-ups with their healthcare provider to monitor their progress, assess the effectiveness of the treatment, and address any concerns or side effects. The frequency of these check-ups will depend on the patient’s individual needs and the doctor’s recommendations.
- Dosage Adjustments: The doctor may need to adjust the dosage of medical marijuana based on the patient’s response to treatment. This may involve increasing or decreasing the dose, changing the frequency of use, or switching to a different form of marijuana.
- Monitoring for Side Effects: Patients should report any side effects they experience to their doctor. Common side effects include dry mouth, dizziness, and changes in appetite. Serious side effects are rare, but it’s important to monitor for them.
- Assessing Treatment Effectiveness: The doctor will assess the effectiveness of the treatment by monitoring the patient’s symptoms and overall well-being. This may involve asking the patient about their pain levels, sleep quality, and overall quality of life.
- Addressing Interactions and Complications: The doctor will monitor for any potential drug interactions or complications that may arise. They may need to adjust the patient’s other medications or provide additional support.
- Education and Support: The doctor should continue to provide education and support to the patient throughout the treatment process. This includes answering questions, providing guidance, and connecting the patient with other resources.
Investigating the Impact of Medical Marijuana Legalization on Public Health is Essential
Medical marijuana legalization is a topic that sparks passionate debate, particularly when it comes to its effects on public health. It’s a complex issue with both potential benefits and potential drawbacks. Understanding these impacts requires a balanced and thorough examination of the available research, acknowledging the complexities of the subject matter.
Public Health Concerns Related to Medical Marijuana Legalization
The legalization of medical marijuana raises legitimate concerns regarding its potential impact on public health. These concerns often center on the possibility of increased substance abuse and the risk of impaired driving.The fear of increased substance abuse is a significant worry, especially among younger populations. Some studies suggest that the perception of marijuana as harmless, coupled with easier access, could lead to increased rates of marijuana use, potentially paving the way for the use of other illicit substances.
It’s important to note that the link between marijuana use and the progression to other drugs is complex and not fully understood, but it is a concern nonetheless.Impaired driving is another major public health concern. Marijuana, like alcohol, can impair cognitive functions and reaction times, making driving dangerous. Legalization might lead to more drivers under the influence, increasing the risk of accidents and fatalities.Here’s a breakdown of the primary concerns:
- Increased Substance Abuse: Concerns include potential for higher rates of marijuana use, especially among young people, and possible links to the use of other illicit substances.
- Impaired Driving: Marijuana use can impair driving abilities, leading to increased risk of accidents and fatalities.
- Addiction: Although less severe than other substances, addiction is possible and requires treatment.
- Gateway Effect: The concept that marijuana use leads to the use of more dangerous drugs.
Potential Benefits of Medical Marijuana Legalization on Public Health
Beyond the potential downsides, medical marijuana legalization offers the promise of several public health benefits. These include a potential reduction in opioid use and improved access to care for patients suffering from various medical conditions.One of the most compelling arguments in favor of medical marijuana legalization is its potential to reduce opioid use. Studies have shown a correlation between access to medical marijuana and a decrease in opioid prescriptions and overdose deaths.
Patients who use marijuana for pain management may be able to reduce or eliminate their reliance on opioids, which are highly addictive and contribute significantly to the overdose crisis.Improved access to care is another potential benefit. Legalization can make it easier for patients with qualifying conditions to obtain the medicine they need. This can lead to better symptom management, improved quality of life, and reduced reliance on more conventional, and sometimes less effective, treatments.Here are the potential benefits:
- Reduced Opioid Use: Medical marijuana may serve as an alternative to opioids for pain management, potentially reducing opioid prescriptions and overdose deaths.
- Improved Access to Care: Legalization can facilitate access to treatment for patients with qualifying medical conditions.
- Symptom Management: Medical marijuana may help manage symptoms of chronic pain, nausea, and other conditions.
- Economic Benefits: Tax revenue from medical marijuana sales can be used to fund public health programs.
Current Research on the Effects of Medical Marijuana Legalization on Public Health Outcomes, Where is medical marijuana legal
The body of research on the effects of medical marijuana legalization is constantly evolving. It is crucial to examine the available data to gain a comprehensive understanding of the impact on public health. The findings are often nuanced and sometimes contradictory, making a balanced approach critical.The impact of medical marijuana legalization on public health outcomes is complex, and current research presents a mixed picture.
Some studies suggest that legalization may be associated with increased rates of marijuana use, particularly among young people, while others find no significant change. Similarly, the impact on traffic accidents and fatalities is debated, with some studies showing an increase and others showing no change or even a decrease.The data available can be summarized as follows:
- Marijuana Use Rates: Some studies show an increase in marijuana use following legalization, especially among young people. Other studies find no significant change.
- Traffic Accidents: Research on the impact of legalization on traffic accidents and fatalities is mixed, with some studies showing an increase and others showing no change or even a decrease.
- Opioid Use and Overdoses: Some studies suggest a correlation between medical marijuana access and a decrease in opioid prescriptions and overdose deaths.
- Mental Health: The impact of medical marijuana on mental health outcomes is an area of ongoing research, with some studies suggesting potential risks for certain individuals.
It is important to acknowledge the limitations of current research. Many studies are observational and cannot establish cause-and-effect relationships. Furthermore, the regulatory frameworks surrounding medical marijuana vary significantly across different jurisdictions, making it difficult to generalize findings.
Delving into the Future of Medical Marijuana Legalization and Research is Interesting
The landscape of medical marijuana is constantly evolving, with new developments emerging regularly. Understanding where the field is heading requires a look at current trends, ongoing research, and predictions for the future. The information below provides a glimpse into what the future might hold.
Current Trends in Medical Marijuana Legalization Worldwide
Globally, the push for medical marijuana legalization continues, albeit at varying speeds. Several countries and regions are currently reevaluating their laws or are in the process of implementing new regulations.
- Europe: Countries like Germany, Italy, and the United Kingdom have already established medical marijuana programs, and others are following suit. The European Union is also considering harmonization of medical cannabis regulations, which could significantly impact the market. Germany’s program, for instance, has seen a steady increase in prescriptions and patient access, signaling a growing acceptance.
- Latin America: Uruguay and Canada have already legalized recreational use, and several countries are exploring medical use options. Colombia, for example, has developed a robust medical cannabis industry, with cultivation and export licenses available.
- Asia-Pacific: While progress has been slower, some countries are beginning to consider changes. Thailand, for instance, has taken steps to legalize medical marijuana. Australia and New Zealand have already implemented medical cannabis programs, with ongoing discussions around improving patient access.
- United States: While federal legalization remains elusive, the number of states with medical marijuana programs continues to grow. States like New York and Maryland are in the process of establishing robust regulatory frameworks. This piecemeal approach, however, creates inconsistencies and complexities in the industry.
Ongoing Research Efforts Aimed at Understanding the Therapeutic Potential of Medical Marijuana
Scientific exploration of medical marijuana is accelerating, with researchers investigating its potential to treat a wide range of conditions. These studies aim to identify specific compounds and understand how they interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system.
- Pain Management: Research continues to explore the use of cannabinoids for chronic pain relief. Studies are examining the effectiveness of different cannabinoid ratios and delivery methods for conditions like neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. For instance, the University of California, San Diego, is conducting studies on the effectiveness of medical cannabis in managing chronic pain in veterans.
- Neurological Disorders: There’s growing interest in medical marijuana’s potential to treat neurological conditions such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and Alzheimer’s disease. Research is investigating the effects of cannabinoids on seizure frequency, spasticity, and cognitive function. A prominent example is the ongoing research into the use of CBD for treating pediatric epilepsy, as seen in the case of Charlotte Figi, which helped raise awareness and drive research.
- Mental Health: Studies are exploring the use of medical marijuana for anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Researchers are investigating the impact of cannabinoids on mood regulation and the brain’s stress response. Research at the University of Colorado Boulder is investigating the effects of cannabis on PTSD symptoms in veterans.
- Cancer Treatment: Investigations are underway to determine if cannabinoids can help manage cancer symptoms and potentially inhibit tumor growth. Studies are focusing on the use of cannabinoids to alleviate nausea, pain, and appetite loss associated with chemotherapy. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) provides detailed information on cannabinoid research and its potential benefits in cancer treatment.
A Forecast for the Future of the Medical Marijuana Industry, Including Potential Innovations and Challenges
The medical marijuana industry is poised for significant growth, but it will face various challenges as it matures. The future will likely see new innovations and shifts in the market.
- Technological Advancements: Expect to see advancements in cultivation techniques, extraction methods, and delivery systems. Precision agriculture, using data analytics and controlled environments, will optimize cannabis cultivation. Sophisticated extraction methods will isolate specific cannabinoids for targeted treatments. New delivery methods, such as inhalers, patches, and edibles with precise dosing, will enhance patient experience and efficacy.
- Market Expansion and Consolidation: The industry will likely see continued expansion as more countries and regions legalize medical marijuana. This growth will also drive consolidation, with larger companies acquiring smaller ones. Increased competition will necessitate innovation and efficiency to stay competitive.
- Regulatory Frameworks: The development of clear and consistent regulatory frameworks will be crucial for the industry’s growth. These frameworks will need to address issues such as product safety, quality control, and patient access. Clear guidelines on advertising and labeling will also be necessary to protect consumers.
- Research and Development: Increased investment in research and development will lead to a deeper understanding of the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids. This will result in the development of new treatments and therapies for a wider range of conditions.
- Challenges: The industry will continue to face challenges, including the need for federal legalization in countries like the United States, as well as the ongoing need to combat the stigma associated with cannabis. Access to financial services and the development of standardized testing protocols are other key challenges.
